|
.jpg)
中文
Introduction
This section is
intended as an introduction and aid to help recognize Chinese characters in the
lexicon.
Chinese language uses a logographic script composed of visual elements arranged
in a variety of ways, rather than the segmental phoneme principle of
construction used in alphabetic languages. Its logograms or ideograms are known
as characters which in turn can be decomposed into components called radicals.
The most commonly accepted table of radicals for traditional Chinese characters
consists of 214 entries which were popularized in the reign of Qing emperor
Kangxi (1716 AD), who commissioned what is now known as the Kangxi Zidian, a character
dictionary listing 47,035 entries. The most
comprehensive dictionary available to date is the Zhonghua Zihai which was
published in 1994 and lists 85,568 characters.
Note however that
just about 3,000 characters are needed for basic literacy (e.g., to read a
Chinese newspaper) and a well-educated person will know around 4,000 to 5,000
characters. Whilst some radicals are characters in
their own right, most are not, but learning them will enable one to recognize
these radicals which in turn will help in the learning and recognition of other
characters. Some radicals have more than one form: they may be used as
side-radicals or have a variant or simplified form. If applicable, this is also
listed below. Chinese was traditionally written vertically, i.e. from top
to bottom, due to the fact that prior to the invention of paper, books in
Ancient China were written on strips of flattened
bamboo, joined together with thread
into long rows that could be rolled up into cylinders and wrapped in cloth. Then later on,
it was also written from right to left, though in 1954, the official
writing system changed and is nowadays from left to right, along with the
movement from Traditional to Simplified characters. See also
Chinese Character Formation & Etymology
and
Comparative Language List.
回
Radicals
| No. |
Radical |
Variants |
Simplified Radical |
Chinese Name |
English Name |
Stroke Count |
|
|
一 |
|
|
yi1 |
one |
1
|
|
|
丨 |
|
|
gun3 |
line |
1
|
|
|
丶 |
|
|
zhu3 |
dot |
1
|
|
|
丿 |
乀, 乁 |
|
pie1 (fu2) (yi2) |
slash |
1
|
|
|
乙 |
乚,
乛 |
|
yi3 (yin3) (zhe2) |
second |
1
|
|
|
亅 |
|
|
jue2 |
hook |
1
|
|
|
二 |
|
|
er4 |
two |
2
|
|
|
亠 |
|
|
tou2 |
lid |
2
|
|
|
人 |
亻 |
|
ren2 |
man |
2
|
|
10
|
儿 |
|
|
er2 |
legs, son |
2
|
|
11
|
入 |
|
|
ru4 |
enter |
2
|
|
|
八 |
丷 |
|
ba1 |
eight |
2
|
|
|
冂 |
|
|
jiong1 |
down box |
2
|
|
|
冖 |
|
|
mi4 |
cover |
2
|
|
|
冫 |
|
|
bing1 |
ice |
2
|
|
16
|
几 |
|
|
ji1 |
table |
2
|
|
17
|
凵 |
|
|
qu3 |
open box |
2
|
|
|
刀 |
刂 |
|
dao1 |
knife |
2
|
|
|
力 |
|
|
li4 |
power |
2
|
|
|
勹 |
|
|
bao1 |
wrap |
2
|
|
|
匕 |
|
|
bi3 |
spoon |
2
|
|
22
|
匚 |
|
|
fang1 |
right open box |
2
|
|
23
|
匸 |
|
|
xi3 |
hiding enclosure |
2
|
|
|
十 |
|
|
shi2 |
ten |
2
|
|
|
卜 |
|
|
bu3 |
Mysticism |
2
|
|
26
|
卩 |
|
|
jie2 |
seal |
2
|
|
|
厂 |
|
|
han4 |
cliff |
2
|
|
28
|
厶 |
|
|
si1 |
private |
2
|
|
|
又 |
|
|
you4 |
again |
2
|
|
|
口 |
|
|
kou3 |
mouth |
3
|
|
|
囗 |
|
|
wei2 |
enclosure |
3
|
|
|
土 |
|
|
tu3 |
earth |
3
|
|
33
|
士 |
|
|
shi4 |
scholar |
3
|
|
|
夂 |
|
|
zhi (top) |
go |
3
|
|
|
夊 |
|
|
sui1 (bottom) |
go slowly |
3
|
|
36
|
夕 |
|
|
xi4 |
evening |
3
|
|
|
大 |
|
|
da4 |
big |
3
|
|
|
女 |
|
|
nü3 |
woman |
3
|
|
|
子 |
|
|
zi3 |
child |
3
|
|
|
宀 |
|
|
mian2 |
roof |
3
|
|
41
|
寸 |
|
|
cun4 |
inch |
3
|
|
|
小 |
|
|
xiao3 |
small |
3
|
|
43
|
尢 |
尣 |
|
wang1 |
lame |
3
|
|
44
|
尸 |
|
|
shi1 |
corpse |
3
|
|
45
|
屮 |
|
|
che4 |
sprout |
3
|
|
46
|
山 |
|
|
shan1 |
mountain |
3
|
|
|
川 |
巛,
巜 |
|
chuan1 (gui4) |
river |
3
|
|
48
|
工 |
|
|
gong1 |
work |
3
|
|
49
|
己 |
|
|
ji3 |
oneself |
3
|
|
50
|
巾 |
|
|
jin1 |
turban |
3
|
|
|
干 |
|
|
gan1 |
dry |
3
|
|
52
|
幺 |
|
|
yao1 |
short thread |
3
|
|
|
广 |
|
|
yan3 |
dotted cliff |
3
|
|
54
|
廴 |
|
|
yin3 |
long stride |
3
|
|
55
|
廾 |
|
|
gong3 |
two hands |
3
|
|
56
|
弋 |
|
|
yi4 |
shoot |
3
|
|
57
|
弓 |
|
|
gong1 |
bow |
3
|
|
58
|
彐 |
彑 |
|
ji4 |
snout |
3
|
|
59
|
彡 |
|
|
shan1 |
bristle |
3
|
|
60
|
彳 |
|
|
chi4 |
step |
3
|
|
|
心 |
忄 |
|
xin1 |
heart |
4
|
|
|
戈 |
|
|
ge1 |
halberd |
4
|
|
63
|
戶 |
|
|
hu4 |
door |
4
|
|
|
手 |
扌 |
|
shou3 |
hand |
4
|
|
65
|
支 |
|
|
zhi1 |
branch |
4
|
|
66
|
攴 |
攵 |
|
pu1 |
rap |
4
|
|
67
|
文 |
|
|
wen2 |
script |
4
|
|
68
|
斗 |
|
|
dou3 |
dipper |
4
|
|
69
|
斤 |
|
|
jin1 |
axe |
4
|
|
|
方 |
|
|
fang1 |
square |
4
|
|
71
|
无 |
|
|
wu2 |
not |
4
|
|
|
日 |
|
|
ri4 |
sun |
4
|
|
|
曰 |
|
|
yue1 |
say |
4
|
|
|
月 |
|
|
yue4 |
moon |
4
|
|
|
木 |
|
|
mu4 |
tree |
4
|
|
76
|
欠 |
|
|
qian4 |
lack |
4
|
|
|
止 |
|
|
zhi3 |
stop |
4
|
|
78
|
歹 |
|
|
dai3 |
death |
4
|
|
|
殳 |
|
|
shu1 |
weapon |
4
|
|
80
|
毋 |
|
|
mu2 |
do not |
4
|
|
81
|
比 |
|
|
bi3 |
compare |
4
|
|
82
|
毛 |
|
|
mao2 |
fur |
4
|
|
83
|
氏 |
|
|
shi4 |
clan |
4
|
|
84
|
气 |
|
|
qi4 |
steam |
4
|
|
|
水 |
氵 |
|
shui3 |
water |
4
|
|
86
|
火 |
灬 |
|
huo3 |
fire |
4
|
|
|
爪 |
爫 |
|
zhao3 |
claw |
4
|
|
88
|
父 |
|
|
fu4 |
father |
4
|
|
89
|
爻 |
|
|
yao2 |
double x |
4
|
|
90
|
爿 |
|
|
qiang2 |
half tree trunk |
4
|
|
91
|
片 |
|
|
pian4 |
slice |
4
|
|
92
|
牙 |
|
|
ya2 |
fang |
4
|
|
93
|
牛 |
牜 |
|
niu2 |
cow |
4
|
|
94
|
犬 |
犭 |
|
quan3 |
dog |
4
|
|
95
|
玄 |
|
|
xuan2 |
profound |
5
|
|
|
玉 |
王 |
|
yu4, wang2 |
jade, king |
5
|
|
97
|
瓜 |
|
|
gua1 |
melon |
5
|
|
98
|
瓦 |
|
|
wa3 |
tile |
5
|
|
99
|
甘 |
|
|
gan1 |
sweet |
5
|
|
100
|
生 |
|
|
sheng1 |
life |
5
|
|
101
|
用 |
|
|
yong4 |
use |
5
|
|
|
田 |
|
|
tian2 |
field |
5
|
|
103
|
疋 |
|
|
pi3 |
bolt of cloth |
5
|
|
104
|
疒 |
|
|
chuang2 |
sickness |
5
|
|
105
|
癶 |
|
|
bo4 |
dotted tent |
5
|
|
106
|
白 |
|
|
bai2 |
black |
5
|
|
107
|
皮 |
|
|
pi2 |
skin |
5
|
|
108
|
皿 |
|
|
min3 |
dish |
5
|
|
109
|
目 |
|
|
mu4 |
eye |
5
|
|
110
|
矛 |
|
|
mao2 |
spear |
5
|
|
|
矢 |
业 |
|
shi3, ye4 |
arrow, business |
5
|
|
112
|
石 |
|
|
shi2 |
stone |
5
|
|
|
示 |
礻 |
|
shi4 |
spirit |
5
|
|
114
|
禸 |
|
|
rou3 |
track |
5
|
|
115
|
禾 |
|
|
he2 |
grain |
5
|
|
116
|
穴 |
|
|
xue4 |
cave |
5
|
|
|
立 |
|
|
li4 |
stand |
5
|
|
118
|
竹 |
⺮ |
|
zhu2 |
bamboo |
6
|
|
119
|
米 |
|
|
mi3 |
rice |
6
|
|
120
|
糸 |
|
纟 |
mi4, si1 |
silk |
6
|
|
121
|
缶 |
|
|
fou3 |
jar |
6
|
|
122
|
网 |
罒 |
|
wang3 |
net |
6
|
|
123
|
羊 |
|
|
yang2 |
sheep |
6
|
|
124
|
羽 |
|
|
yu3 |
feather |
6
|
|
125
|
老 |
|
|
lao3 |
old |
6
|
|
126
|
而 |
|
|
er2 |
and |
6
|
|
127
|
耒 |
|
|
lei3 |
plow |
6
|
|
128
|
耳 |
|
|
er3 |
ear |
6
|
|
129
|
聿 |
|
|
yu4 |
brush |
6
|
|
|
肉 |
|
|
rou4 |
meat |
6
|
|
131
|
臣 |
|
|
chen2 |
minister |
6
|
|
132
|
自 |
|
|
zi4 |
self |
6
|
|
133
|
至 |
|
|
zhi4 |
arrive |
6
|
|
134
|
臼 |
|
|
jiu4 |
mortar |
6
|
|
135
|
舌 |
|
|
she2 |
tongue |
6
|
|
136
|
舛 |
|
|
chuan3 |
oppose |
6
|
|
137
|
舟 |
|
|
zhou1 |
boat |
6
|
|
138
|
艮 |
|
|
gen4 |
stopping |
6
|
|
139
|
色 |
|
|
se4 |
colour |
6
|
|
|
艸 |
艹 |
|
cao3 |
grass |
6
|
|
141
|
虍 |
|
|
hu1 |
tiger |
6
|
|
142
|
虫 |
|
|
chong2 |
insect |
6
|
|
143
|
血 |
|
|
xue3 |
blood |
6
|
|
144
|
行 |
|
|
xing2, hang2 |
walk, profession |
6
|
|
145
|
衣 |
衤 |
|
yi1 |
clothes |
6
|
|
|
襾 |
覀,
西 |
|
ya4, xi1 |
cover, west |
6
|
|
147
|
見 |
|
见 |
jian4 |
see |
7
|
|
148
|
角 |
|
|
jue2 |
horn |
7
|
|
149
|
言 |
|
讠 |
yan2 |
speech |
7
|
|
150
|
谷 |
|
|
gu3 |
valley |
7
|
|
151
|
豆 |
|
|
dou4 |
bean |
7
|
|
|
豕 |
|
|
shi3 |
pig |
7
|
|
153
|
豸 |
|
|
zhi4 |
badger |
7
|
|
154
|
貝 |
|
贝 |
bei4 |
shell |
7
|
|
155
|
赤 |
|
|
chi4 |
red |
7
|
|
156
|
走 |
|
|
zou3 |
run |
7
|
|
157
|
足 |
|
|
zu2 |
foot |
7
|
|
158
|
身 |
|
|
shen1 |
body |
7
|
|
159
|
車 |
|
车 |
che1 |
cart |
7
|
|
160
|
辛 |
|
|
xin1 |
bitter |
7
|
|
161
|
辰 |
|
|
chen2 |
morning |
7
|
|
162
|
辵 |
辶 |
|
chuo4 |
walk |
7
|
|
163
|
邑 |
阝(right) |
|
yi4 |
city |
7
|
|
164
|
酉 |
|
|
you3 |
wine |
7
|
|
165
|
釆 |
|
|
bian4 |
distinguish |
7
|
|
166
|
里 |
|
|
li3 |
village |
7
|
|
|
金 |
钅 |
|
jin1 |
gold |
8
|
|
168
|
長 |
|
长 |
chang2 |
long |
8
|
|
|
門 |
|
门 |
men2 |
gate |
8
|
|
170
|
阜 |
阝(left) |
|
fu4 |
mound |
8
|
|
171
|
隶 |
|
|
dai4 |
slave |
8
|
|
172
|
隹 |
|
|
zhui1 |
short tailed bird |
8
|
|
173
|
雨 |
|
|
yu3 |
rain |
8
|
|
174
|
青 |
|
|
qing1 |
blue |
8
|
|
175
|
非 |
|
|
fei1 |
wrong |
8
|
|
176
|
面 |
|
|
mian4 |
face |
9
|
|
177
|
革 |
|
|
ge2 |
leather |
9
|
|
178
|
韋 |
|
韦 |
wei2 |
tanned leather |
9
|
|
179
|
韭 |
|
|
jiu3 |
leek |
9
|
|
180
|
音 |
|
|
yin1 |
sound |
9
|
|
181
|
頁 |
|
页 |
ye4 |
leaf |
9
|
|
182
|
風 |
|
风 |
feng1 |
wind |
9
|
|
183
|
飛 |
|
飞 |
fei1 |
fly |
9
|
|
184
|
食 |
飠 |
饣 |
shi2 |
eat |
9
|
|
185
|
首 |
|
|
shou3 |
head |
9
|
|
186
|
香 |
|
|
xiang1 |
fragrant |
9
|
|
187
|
馬 |
|
马 |
ma3 |
horse |
10
|
|
188
|
骨 |
|
|
gu3 |
bone |
10
|
|
189
|
高 |
|
|
gao1 |
tall |
10
|
|
190
|
髟 |
|
|
biao1 |
hair |
10
|
|
191
|
鬥 |
|
|
dou4 |
fight |
10
|
|
192
|
鬯 |
|
|
chang4 |
sacrificial wine |
10
|
|
193
|
鬲 |
|
|
li4 |
cauldron |
10
|
|
194
|
鬼 |
|
|
gui3 |
ghost |
10
|
|
195
|
魚 |
|
鱼 |
yu2 |
fish |
11
|
|
196
|
鳥 |
|
鸟 |
niao3 |
bird |
11
|
|
197
|
鹵 |
|
|
lu3 |
salt |
11
|
|
198
|
鹿 |
|
|
lu4 |
deer |
11
|
|
199
|
麥 |
|
麦 |
mai4 |
wheat |
11
|
|
200
|
麻 |
|
|
ma2 |
hemp |
11
|
|
201
|
黃 |
|
|
huang2 |
yellow |
12
|
|
202
|
黍 |
|
|
shu3 |
millet |
12
|
|
203
|
黑 |
|
|
hei1 |
black |
12
|
|
204
|
黹 |
|
|
zhi3 |
embroidery |
12
|
|
205
|
黽 |
|
黾 |
min3 |
frog |
13
|
|
206
|
鼎 |
|
|
ding3 |
tripod |
13
|
|
207
|
鼓 |
|
|
gu3 |
drum |
13
|
|
208
|
鼠 |
|
鼡 |
shu3 |
rat |
13
|
|
209
|
鼻 |
|
|
bi2 |
nose |
14
|
|
210
|
齊 |
|
齐 |
qi2 |
even |
14
|
|
211
|
齒 |
|
齿 |
chi3 |
tooth |
15
|
|
212
|
龍 |
|
龙 |
long2 |
dragon |
16
|
|
213
|
龜 |
|
龟 |
gui1 |
turtle |
16
|
|
214
|
龠 |
|
|
yue4 |
flute |
17
|
Numerals
| |
一
..... 1
二
..... 2
三
..... 3
四
..... 4
五
..... 5 |
六
..... 6
七
..... 7
八
..... 8
九 ..... 9
十 ..... 10 |
|
Phonetic
Transcription (Zhuyin)
~ Consonants
|
ㄗ |
ㄓ |
ㄐ |
ㄍ |
ㄉ |
ㄅ |
|
z |
zh |
j |
g |
d (t) |
b (p) |
|
ㄘ |
ㄔ |
ㄑ |
ㄎ |
ㄊ |
ㄆ |
|
c |
ch |
q |
k |
t |
p (ph) |
|
ㄙ |
ㄕ |
ㄒ |
ㄏ |
ㄋ |
ㄇ |
|
s |
sh |
x (s) |
h |
n |
m |
| |
ㄖ |
|
|
ㄌ |
ㄈ |
| |
r |
|
|
l |
f |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
~ Vowels
|
|
|
|
|
| |
ㄦ |
ㄢ |
ㄞ |
ㄚ |
ㄧ / l |
| |
er (eu) |
an |
ai |
a |
i |
| |
|
ㄣ |
ㄟ |
ㄛ |
ㄨ |
| |
|
en (eun) |
ei (eij) |
o |
u (oe) |
| |
|
ㄤ |
ㄠ |
ㄜ |
ㄩ |
| |
|
ang |
ao |
e (eu) |
u (yu/ü) |
| |
|
ㄥ |
ㄡ |
ㄝ |
|
| |
|
eng/ong/-ng |
ou (ow) |
e |
|
Tones (marks or digits)
Mandarin Chinese has five tones.
These tones are the high level tone; high rising tone;
low falling-rising tone; high falling tone;
and the neutral tone. To represent these
tones the pinyin system uses either diacritics or adds
a digit to the end of each individual syllable. The number used for each tone is
as the order listed below, except for the neutral tone which is usually not numbered.
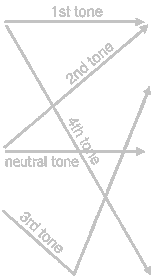 |
|
1. The High Level Tone is marked
by a macron (ˉ): 妈 (mā/ma1) mother
2. The (High) Rising Tone is marked
by an acute accent (ˊ): 麻 (má/ma2) hemp
3. The (Low) Falling-Rising is
marked by a caron/háček (ˇ): 马 (mǎ/ma3) horse
4. The (High) Falling Tone is
marked by a grave accent (ˋ): 骂 (mà/ma4) scold
5. The Neutral Tone is represented without any accent mark: 吗 (ma) question particle
|
回





|

.jpg)

